18.IdentityServer4中的修改密码、登出等.md 14KB
了解IdentityServer4的原理
首先在请求管道里有一个有关IdentityServer4的中间件,通过这个中间件来设施所有有关IdentityServer4的逻辑。
app.UseIdentityServer();
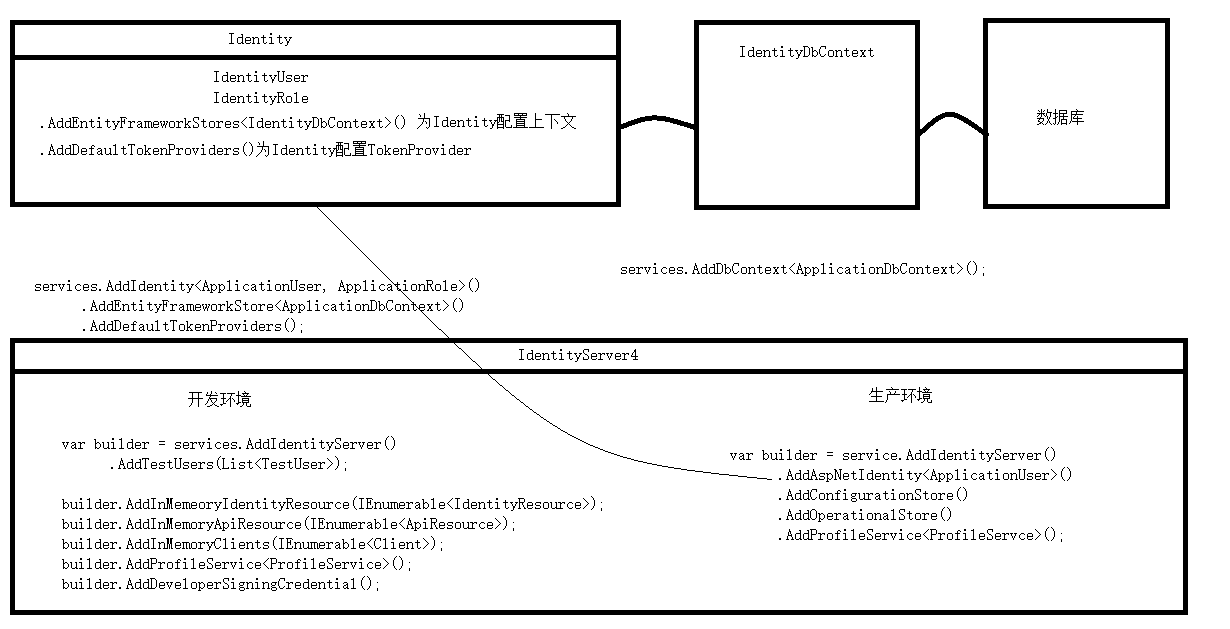
在DI容器里通过services.AddDbContext<IdentityDbContext>()有了上下文,通过services.AddIdentity<IdentityUser, IdentityRole>有了Identity,通过services.AddIdentityServer()有了IdentityServer4。其中的关系用图表示就是:
IdentityServer4掌管着所有的用户。
public static IENumerable<TestUser> GetUsers()
{
return enw List<TestUser>{
new TestUser{
SubjectId="1",
Username = "",
Passowrd=""
Claims = {
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Name,""),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.GivenName,""),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.FamilyName,""),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Email, ""),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.EmailVerified, "true", ClaimValueTypes.Boolean),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.WebSite, ""),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Address,@"", IdentityServer4.IdentityServerConstancts.ClaimValueTypes.Json),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, GlobalSetting.Temp_Role_Manager),
new Claim("GroupId","1")
}
}
};
}
以上GroupId是如何加上的呢?是通过IProfileService这个接口加上的。
public class ProfielService : IProfileService
{
private readonly IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory<ApplicationUser> _claimsFactory;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
private readonly IHostingEnvironment _hostingEnvironment;
//构造函数略
public async Task GetProfileDataAsync(ProfileDataRequest context)
{
if(_hostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
context.IssuedClaims.AddRange(context.Subject.Claims);
}
else
{
//获取用户的SubjectId
var sub = context.Subject.GetSubjectId();
//获取用户
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(sub);
//获取用户的ClaimsPrincipal
var claims = await _claimsFactory.CreateAsync(user);
//获取用户的所有claim
var claims = principal.Claims.ToList();
claims = claims.Where(claim => context.RequestedClaimTypes.Contains(claim.Type)).ToList();
claims.Add(new Claim("GroupId", user.GroupId));
context.IssuedClaims = claims;
}
}
public async Task IsActiveAsync(IsActiveContext context)
{
if(!_hostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
var sub = context.Subject.GetSubjectId();
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(sub);
context.IsActive = user != null;
}
}
}
以上,在上下文中有一个类型为ClaimsPrincipal的Subject属性,从ClaimsPricipal的GetSubjectId方法可以获取string类型的编号,把这个编号交给UserManager就获取到用户,把用户交给IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory获取ClaimsPrincipal,在其中包含所有的Claim。也就是:
- 从上下文获取SubjectId
- 从
UserManager获取User - 从
IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory获取ClaimsPrincipal - 从
ClaimsPrincipal获取Claims
IdentityServer4管理着所有的IdentityResource
public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources()
{
return new List<IdentityResource>{
new IdentityResource.OpenId(),
new IdentityResource.Profile(),
new IdentityResource.Address(),
new IdentityResource.Phone(),
new IdentityResource.Email(),
new IdentityResource("roles","角色",new List<string>{JwtClaimTypes.Role})
};
}
IdentityServer4管理着所有的ApiResource
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources()
{
return new List<ApiResource>{
new ApiResource("for_moble","")
};
}
IdentityServer4管理着所有的Client
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients()
{
return new List<Client>{
new Client{
ClientId = "",
ClientSecrets = new List<Secret>{},
AllowedGrantTYpes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassowrd,
AllowedScopes = new List<string>{
"for_mobile",
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Address,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Phone,
"roles" //这里和IdentityResource中的对应
}
}
};
}
种子数据是如何加上的呢?
var host = CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build();
using(var scope = host.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
var userManager = services.GetRequestService<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>();
var roleManager = services.GetRequiredServce<RoleManager<ApplicationRole>>();
SeedData.EnsureSeedData(servcies, userManager, roleManager).Wait();
}
host.Run();
接着往下走
public static async Task EnsureSeedData(IServiceProvider serviceProvider, UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager, RoleManager<ApplicationRole> roleManager)
{
//先保证所有的上下文数据库完成了迁移
serviceProvider.GetRequestSerivce<ApplicationDbContext>().Database.Migrate();
serviceProvider.GetRequredService<ConfigurationDbContext>().Database.Migrate();
serviceProvider.GetRequriedService<PersistedGrantDbContext>().Database.Migrate();
//确认和ConfigurationDbContext相关的几张表
if(!context.Clients.Any())
{
}
if(!context.IdentityResources.Any())
{
}
if(!context.ApiResources.Any())
{
}
//种子化用户数据
if(!serviceProvider.GetRequredService<ApplicationDbContext>.Users.Any)
{
}
}
最后客户端需要配置认证服务器。
services.AddAuthentication();
app.UseAuthentication();
看一个例子
在stackoverflow上提到了这样一个问题:有一台IdentityServer4的验证服务器,有多个Client, 当在某个Client的API中重置密码产生新的token,这个token在其它client就不生效了。
更新密码产生新的token的写法:
var token = await _userManager.GeneratePasswordResetTokenAsync(appUser);
IdentityServer4的配置:
var migrationAssembly = typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.GetName().Name;
services
.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>(options => {
options.Lockout.AllowedForNewUsers = true;
options.Lockout.DefaultLockoutTimeSpan = new System.TimeSpan(12,0,0);
options.Lockout.MaxFailedAccessAttempts = int.Parse(Configuration["MaxFailedAttempts"]);
})
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTOkenProviders();
var builder = services.AddIdentityServer(options => {
options.Events.RaiseErrorEvents = true;
options.Events.RaiseInformationEvents = true;
options.Events.RaiseFailureEvents = true;
options.Events.RaiseSuccessEvents = ture;
options.Authentication.CookieSlidingExpiration = ture;
})
.AddAspNetIdentity<ApplicationUser>()
.AddConfigurationStore(options => {
options.ConfigureDbContext = b =>
b.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MirationsAssembly(migrationAssembly));
options.DefaultSchemma = Globals.Some;
})
.AddOperationalStore(options => {
options.ConfigureDbContext = b =>
b.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationAssembly(migrationAssembly));
options.DefaultSchema = "";
opitions.EnalbeTokenCleanup = true;
options.TokenCleanupInterval = 30;
})
.AddProfileServce<CustomProfileService>()
.AddSigninCredentialFromConfig();
在一个客户端的API的Startup.cs中
services.AddTransient<IUserStore<ApplicationUser>, UserStore<ApplicaitonUser, IdentityRole, ApplicationDBContext>>();
services.AddTransient<IRoleStore<IdentityRole>, RoleStore<IdentityRole, ApplicatioDbContext>>();
services.AddTransient<IPasswordHasher<ApplicationUser>, PasswordHasher<ApplicationUser>>();
services.AddTransient<ILookupNormalizer, UpperInvariantLookupNomalizer>();
servces.AddTransient<IdentityErrorDescriber>();
var identityBuilder = new IdentityBuilder(typeof(Applicationuser), typeof(IdentityRole), services);
identityBuilder.AddTokenProvider("Default", typeof(DataProtectorTokenProvider<ApplicationUser>));
services.AddTransient<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>();
在底下的回复中,让所有客户端的API和IdentityServer4 实例使用同一个ASP.NET Core Data Protection。使用Redis缓存作为分布式缓存,让所有的客户端API和IdentityServer4在创建token的时候使用同样的key。在所有的Startup.cs中:
services.AddSession();
services.Configure<RedisConfiguration>(Configuration.GetSection("redis"));//配置类全局公用
services.AddDistributedRedisCache(options => {
options.Configuration = Configuration.GetValue<string>("redis:host");
});//配置redis
var redis = Connectionmultiplexer.Connect(Configuration.GetValue<string>("redis:host"));
services.AddDataProtection()
.PersisteKeysToRedis(redis, "DataProtection-Keys")
.SetApplicationName();
services.AddTransient<ICacheService, CacheService>();
在客户端API的请求管道中
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseSession();
在IdentityServer4的请求管道中
app.UseIdentityServer();
app.UseSession();
也就是说在生成token的时候和DataProtection有关,让所有的客户端API和IdentityServer4使用同样的key是这里的解决思路。
尝试
在API的项目首先实现IdentityUser接口。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore;
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
public bool IsAmin{get;set;}
public string DataEventRecourdsRole{get;set;}
public string SecuredFilesRole{get;set;}
public DateTime AccountExpires{get;set;}
}
需要把新创建的IdentityUser放到DI容器中,并且配有上下文。
services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options => options.UseSqllite(Configuration.GetConnectionString("")));
services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
在web中创建用户
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
private readonly SignInManager<ApplicationUser> _signInManager;
[HttpPost]
[AllowAnonymous]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActioinResult> Register(RegisterViewModel model, string returnUrl)
{
ViewData["ReturnUrl"] = returnUrl;
if(ModelState.IsValid)
{
var dataEventsRole = "dataEventRecords.user";
var secureFilesRole = "securedFiles.user";
if(model.IsAdmin)
{
dataEventsRole = "dataEventRecourds.admin";
securedFilesRole = "securedFiles.admin";
}
var user = new ApplicationUser{
UserName = model.Email,
Email = model.Email,
IsAdmin = model.IsAdmin,
DataEventRecordsRole = dataEventsRole,
SecuredFilesRole = securedFilesRole,
AccountExpres = DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(7.0)
};
var result = await _userManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password);
if(result.Succeeded)
{
await _signInManager.SignInAsync(user, isPersistent:false);
_logger.LogInformation();
return RedirectToLocal(returnUrl);
}
AddErrors(result);
}
return View(model);
}
在ApplicationUser中添加的属性如果要开放出去给到其它的客户端,需要通过IProfileServce。
public class IdentityWithAdditionalClaimsProfileService : IProfileService
{
private readonly IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory<ApplicationUser> _claimsFactory;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
public async Task GetPfoileDataAsync(ProfileDataRequestContext context)
{
var sub = context.Subject.GetSubjectId();
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(sub);
var principal = await _claimsFactory.CreateAsync(user);
var claims = principal.Claims.ToList();
claims = claims.Where(claim => context.RequestedClaimTypes.Containes(claim.Type)).ToList();
claims.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.GivenName, user.UserName));
if(user.IsAdmin)
{
claims.Add(new Claim(JwtClimTypes.Role, "admin"));
}
else
{
claims.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role,"user"));
}
if(user.DataEventRecordsRole == "dataEventRecords.admin")
{
claims.Add(new Cliam(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "dataEventRecords.admin"));
cliams.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "dataEventRecords.user"));
claims.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "dataEventRecords"));
claims.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Scoe, "dataEventRecords"));
}
else
{
}
claims.Add(new Claim(IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email, user.Email));
context.IssuedClaims = claims;
}
}
以上在ApplicationUser中的属性值被加到了claims中,在Startup中也可以加适当的policy.
services.AddAuthorization(options => {
options.AddPolicy("dataEventRecordsAdmin", policyAdmin => {
policyAdmin.RequireClaim("role","dataEventRecords.admin")
})
})
最后Policy被用到控制器中。
[Authorize("policyname")]
public class SomeController : Controller
接下来提供一个接口给外界调用。 [Authorize] [Produces(“application/json”)] [Route(api/UserManagement)] public class UserManagementController : Controller {
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
public IActionResult Get()
{
var users = _context.Users.ToList();
var result = new List<UserDto>();
return Ok(result);
}
public void Put(string id, [FromBody]UserDto userDto)
{
var user = _context.Users.First(t=>t.Id == id);
user.IsAdmin = userDto.IsAdmin;
if(userDto.IsActive)
{
if(user.AccountExpres < DateTime.UtcNow)
{
user.AccountExpres = DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(7.0);
}
}
else
{
user.AccountExpires = new DateTime();
}
_context.Users.Update(user);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}